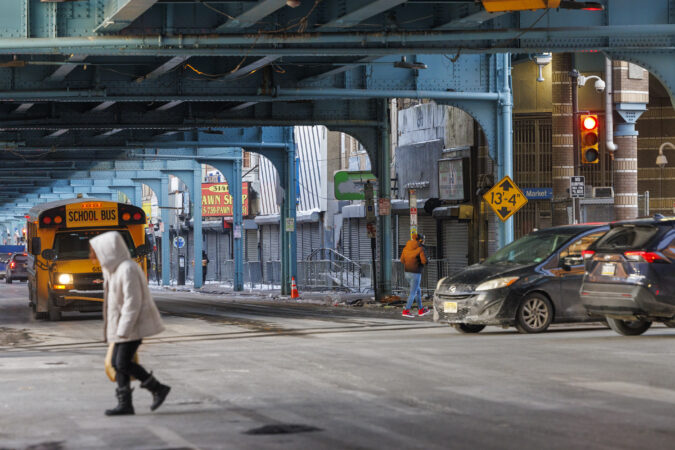
Philadelphia lawmakers are set to consider legislation that would make it harder for ICE to operate in the city, including limiting information sharing, restricting activity on city-owned property, and prohibiting agents from concealing their identities.
Among the package of bills set to be introduced Thursday is an ordinance that effectively makes permanent Philadelphia’s status as a so-called “sanctuary city” by barring city officials from holding undocumented immigrants at ICE’s request without a court order. Another bans discrimination based on immigration status.
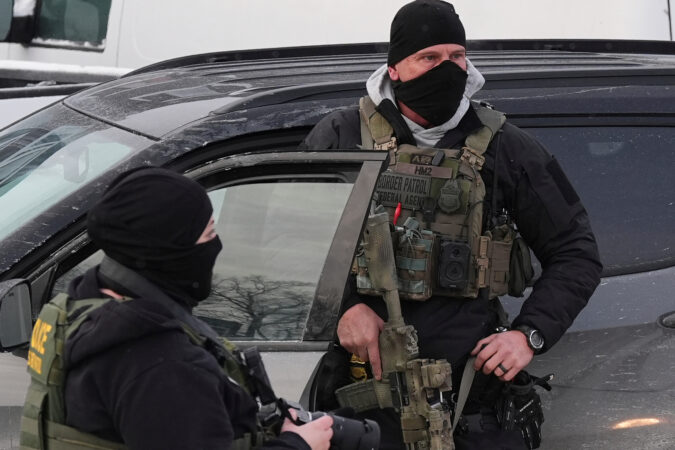
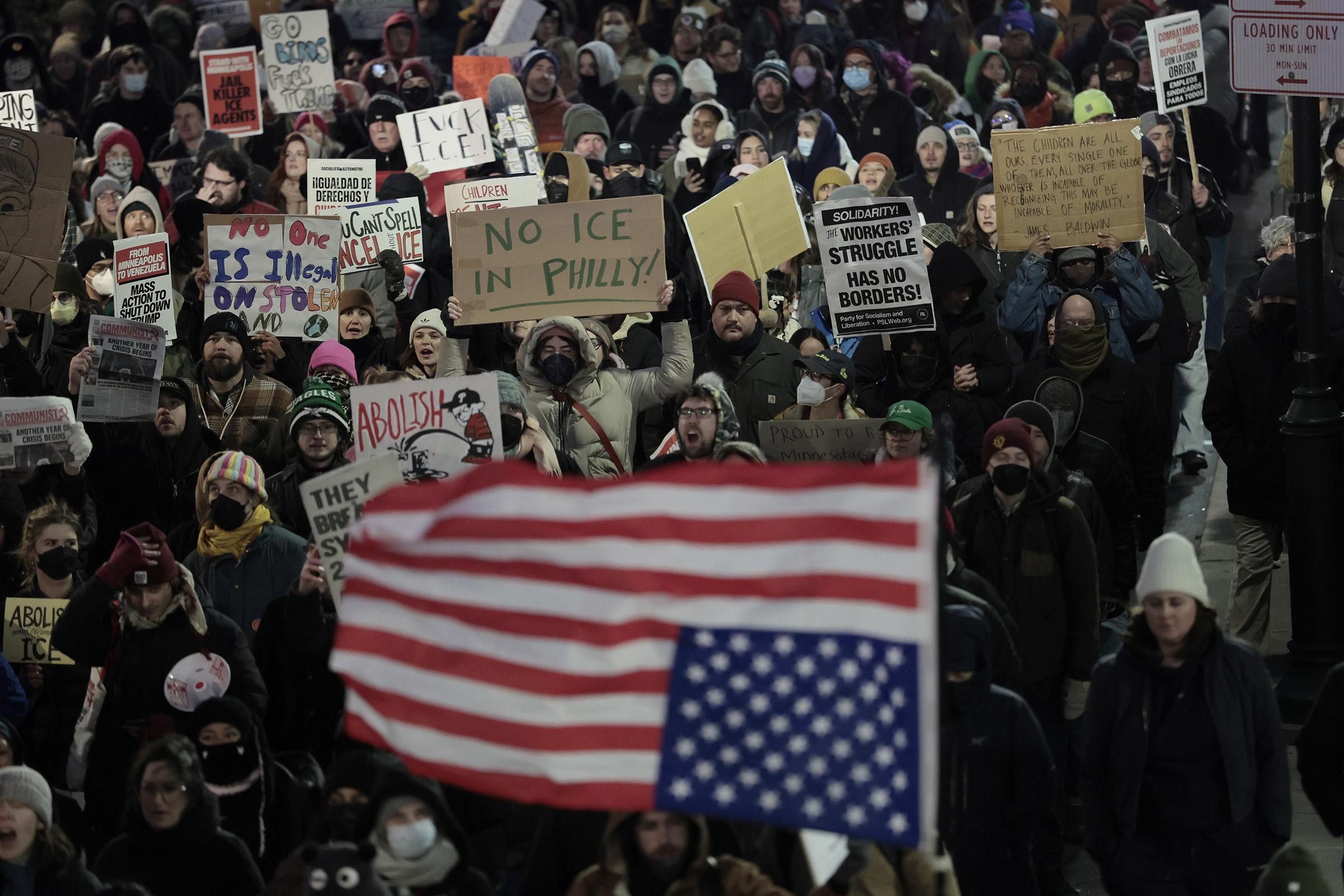
Two City Council members are expected to introduce the legislation as U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement is facing mounting national scrutiny over its tactics in Minneapolis, where federal agents fatally shot two U.S. citizens this month.
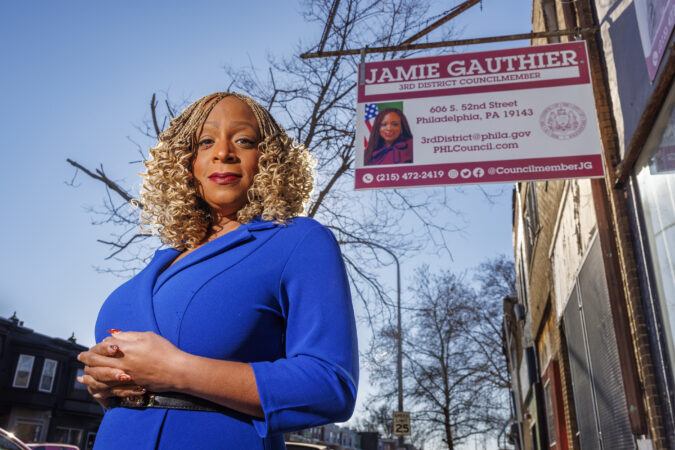
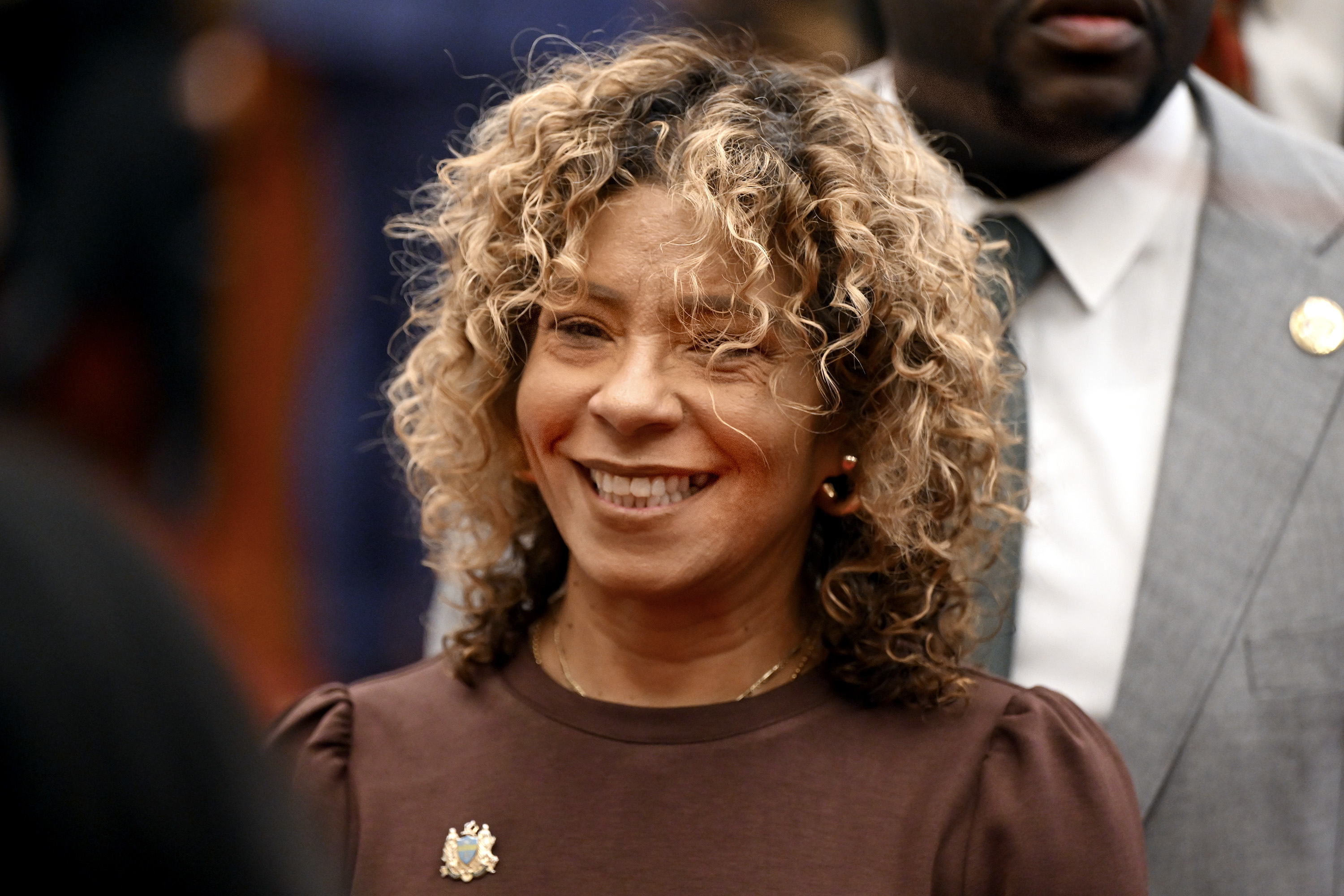
Councilmembers Rue Landau, a Democrat, and Kendra Brooks, of the progressive Working Families Party, said in an interview that the violence in Minneapolis hardened their resolve to introduce legislation to protect a population that includes an estimated 76,000 undocumented immigrants in Philadelphia.
“It’s been very disheartening and frightening to watch ICE act with such lawlessness,” Landau said. “When they rise to the level of killing innocent civilians, unprecedented murders … this is absolutely the time to stand up and act.”
The package of a half-dozen bills is the most significant legislative effort that Council has undertaken to strengthen protections for immigrants since President Donald Trump took office last year on a promise to carry out a mass deportation campaign nationwide.

ICE spokespeople did not immediately reply to a request for comment.
Jasmine Rivera, executive director of the Pennsylvania Immigration Coalition, said it’s not the job nor the jurisdiction of the city to enforce federal law.
The goal of the legislation, Rivera said, is ensuring that “not a single dime and single second of our local resources is being spent collaborating with agencies that are executing people.”
Activists have for months urged Mayor Cherelle L. Parker to formally affirm her commitment to the city’s sanctuary status. Top city officials say an executive order signed by the former mayor to limit the city’s cooperation with ICE remains in place.
But Parker, a centrist Democrat, has taken a quieter approach than her colleagues in Council, largely avoiding criticizing the Trump administration outwardly and saying often that she is focused on her own agenda.
Now, the mayor could be forced to take a side. If City Council passes Landau and Brooks’ legislation this spring, Parker could either sign the bills into law, veto them, or take no action and allow them to lapse into law without her signature. She has never vetoed a bill.
Joe Grace, a spokesperson for Parker, declined to comment on the legislation.

It’s unclear what fate the ICE legislation could meet in Council. The 17-member body has just one Republican, but Parker holds influence with many of the Democrats in the chamber.
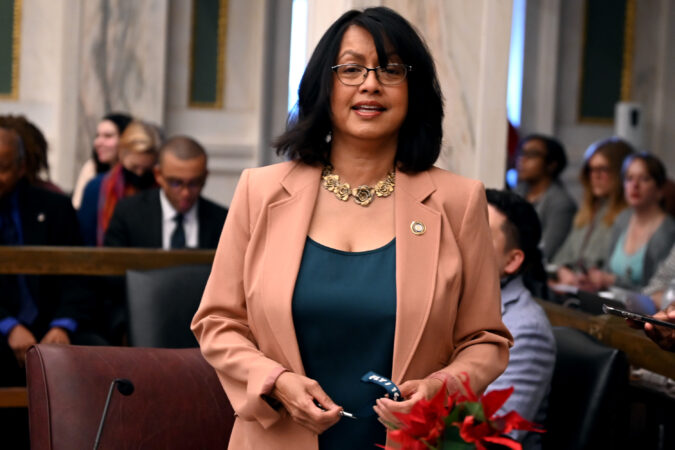
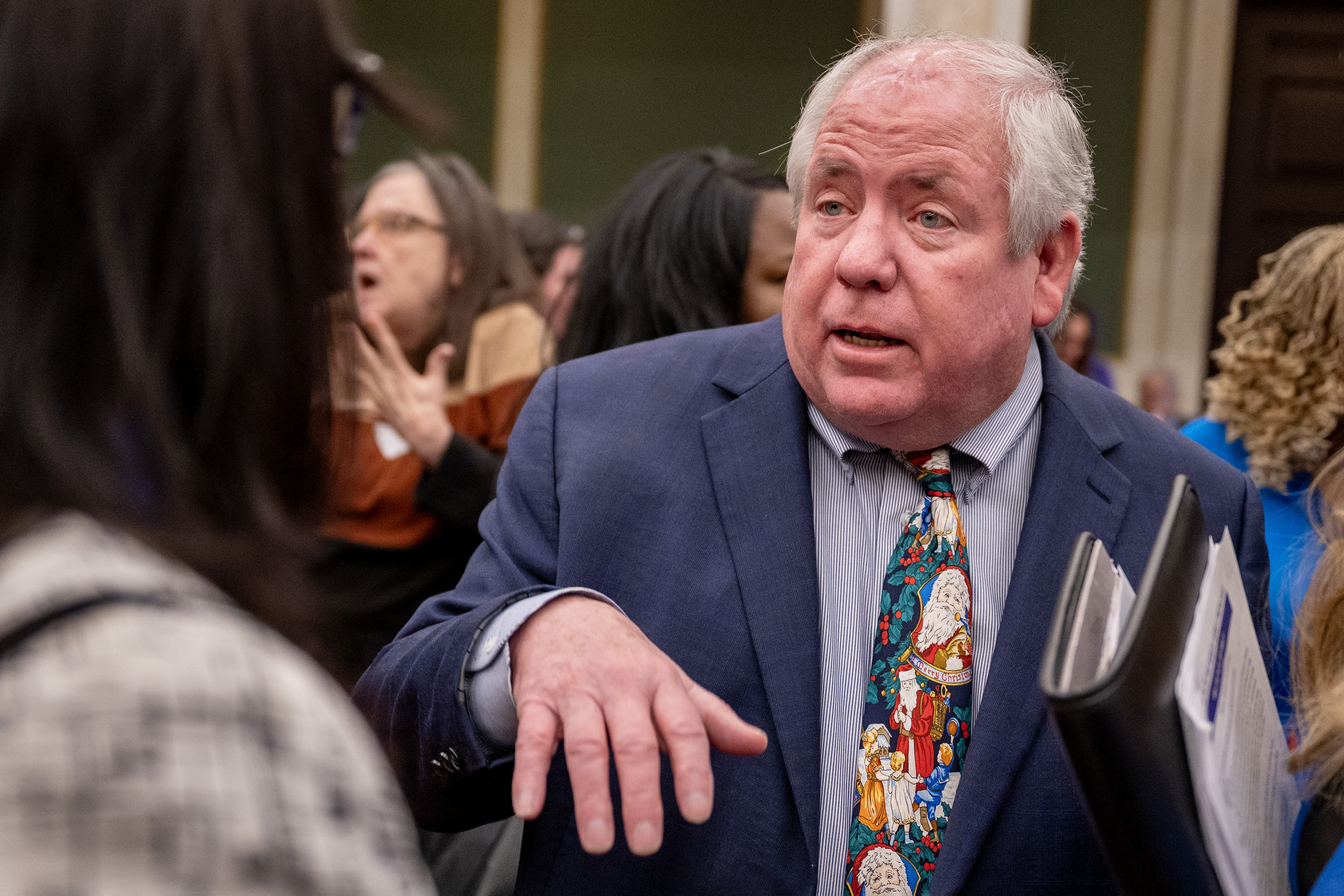
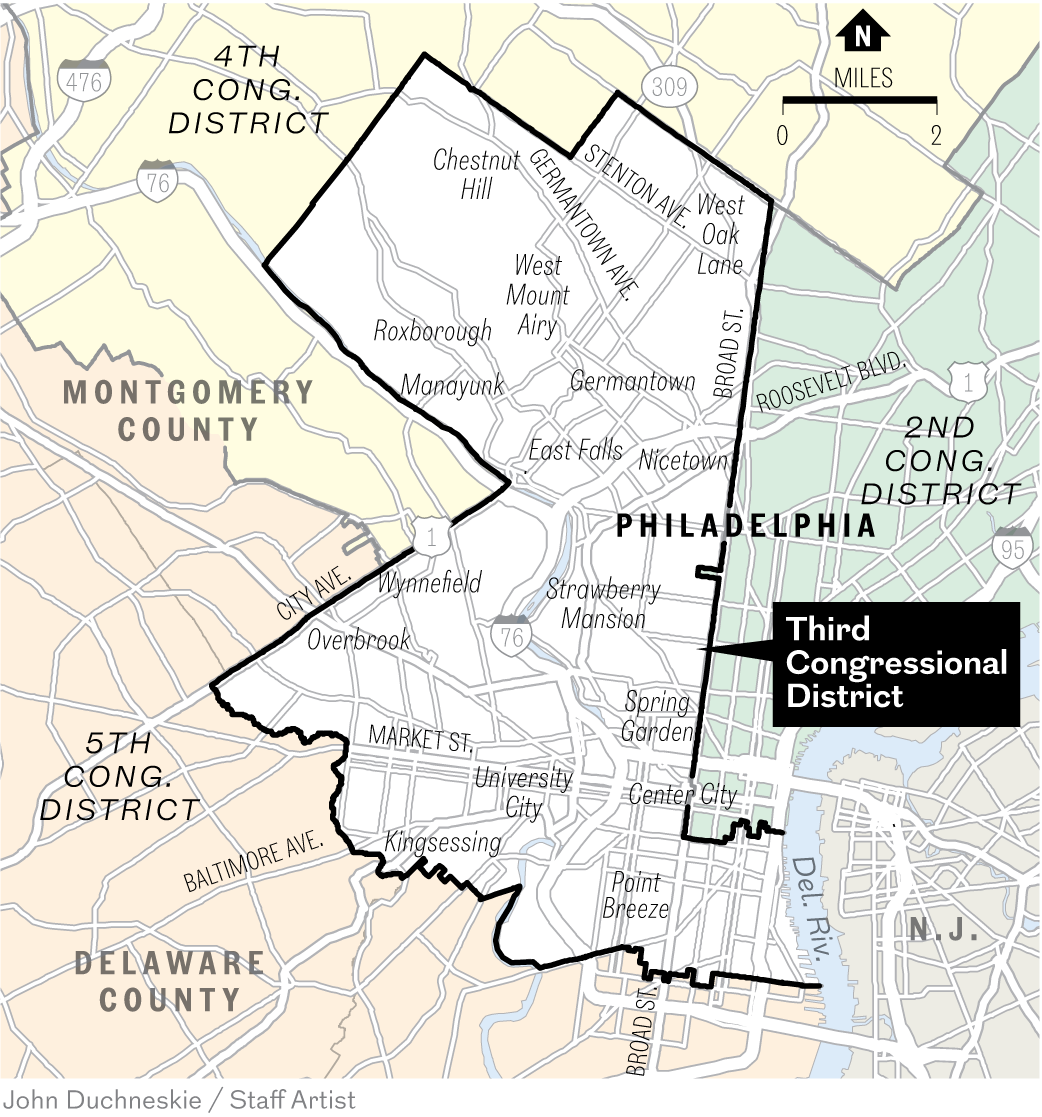
City Council President Kenyatta Johnson, a Democrat who controls the flow of legislation, has not taken a position on the package proposed by Landau and Brooks.
But he said in a statement that “Philadelphia has long positioned itself as a welcoming city that values the contributions of immigrants and strives to protect their rights and safety.”
“I have deep concerns about federal ICE actions directed by President Donald Trump’s administration that sow fear and anxiety in immigrant communities,” Johnson said, “underscoring the belief that enforcement practices should be lawful, humane, and not undermine trust in public safety.”
Making sanctuary status the law
Border Patrol and ICE are both federal immigration agencies, which are legally allowed to operate in public places and subject to federal rules and regulations. Some cities and states — not including Pennsylvania and New Jersey — actively cooperate with ICE through written agreements.
Since 2016, Philadelphia has operated under an executive order signed by former Mayor Jim Kenney, which prohibits city jails from honoring ICE “detainer requests,” in which federal agents ask the city to hold undocumented immigrants in jail for longer than they would have otherwise been in custody to facilitate their arrest by federal authorities.
Undocumented immigrants are not shielded from federal immigration enforcement, nor from being arrested and charged by local police for local offenses.
Some refer to the noncooperation arrangement as “sanctuary.” As the term “sanctuary cities” has become politically toxic, some local officials — including in Philadelphia — have backed away from it, instead declaring their jurisdictions to be “welcoming cities.”
Parker administration officials have said several times over the last year that Philadelphia remains a “welcoming city.”

But advocates for immigrants have said they want an ironclad city policy that can’t be rescinded by a mayor.
Landau and Brooks’ legislation would be that, codifying the executive order into law and adding new prohibitions on information sharing. The package includes legislation to:
- Strengthen restrictions on city workers, including banning local police from carrying out federal immigration enforcement and prohibiting city workers from assisting in enforcement operations.
- Prohibiting law enforcement officers from concealing their identities, including by wearing masks or covering up badges with identifying information.
- Banning ICE from staging raids on city-owned property and designated community spaces such as schools, parks, libraries, and homeless shelters. (It would not apply to the Criminal Justice Center, where ICE has had a presence. The courthouse is overseen by both city and state agencies.)
- Prohibiting city agencies and contractors from providing ICE access to data sets to assist in immigration enforcement.
- Restricting city employees from inquiring about individuals’ immigration status unless required by a court order, or state or federal law.
Peter Pedemonti, co-director of New Sanctuary Movement of Philadelphia, an advocacy organization that partnered with the Council members to craft the package of bills, compared ICE to an octopus that has multiple arms reaching into different facets of American life.
The proposed legislation, he said, is a means to bind a few of those arms.
“The whole world can see the violence and brutality,” Pedemonti said. “This is a moment where all of us need to stand up, and Philadelphia can stand up and speak out loud and clear that we don’t want ICE here to pull our families apart, the families that make Philadelphia Philadelphia.”
An impending showdown that Parker hoped to avoid
Homeland Security officials claim that sanctuary jurisdictions protect criminal, undocumented immigrants from facing consequences while putting U.S. citizens and law enforcement officers in peril.
Last year, the Trump administration named Philadelphia as among the jurisdictions impeding federal immigration enforcement. The White House has said the federal government will cut off funding to sanctuary cities by Feb. 1.
However, the president has made no explicit threat to ramp up ICE activities in Philadelphia.
Some of Parker’s supporters say the mayor’s conflict-averse strategy has spared Philadelphia as other cities such as Washington, New York, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Minneapolis have seen National Guard troops or waves of ICE agents arrive in force.
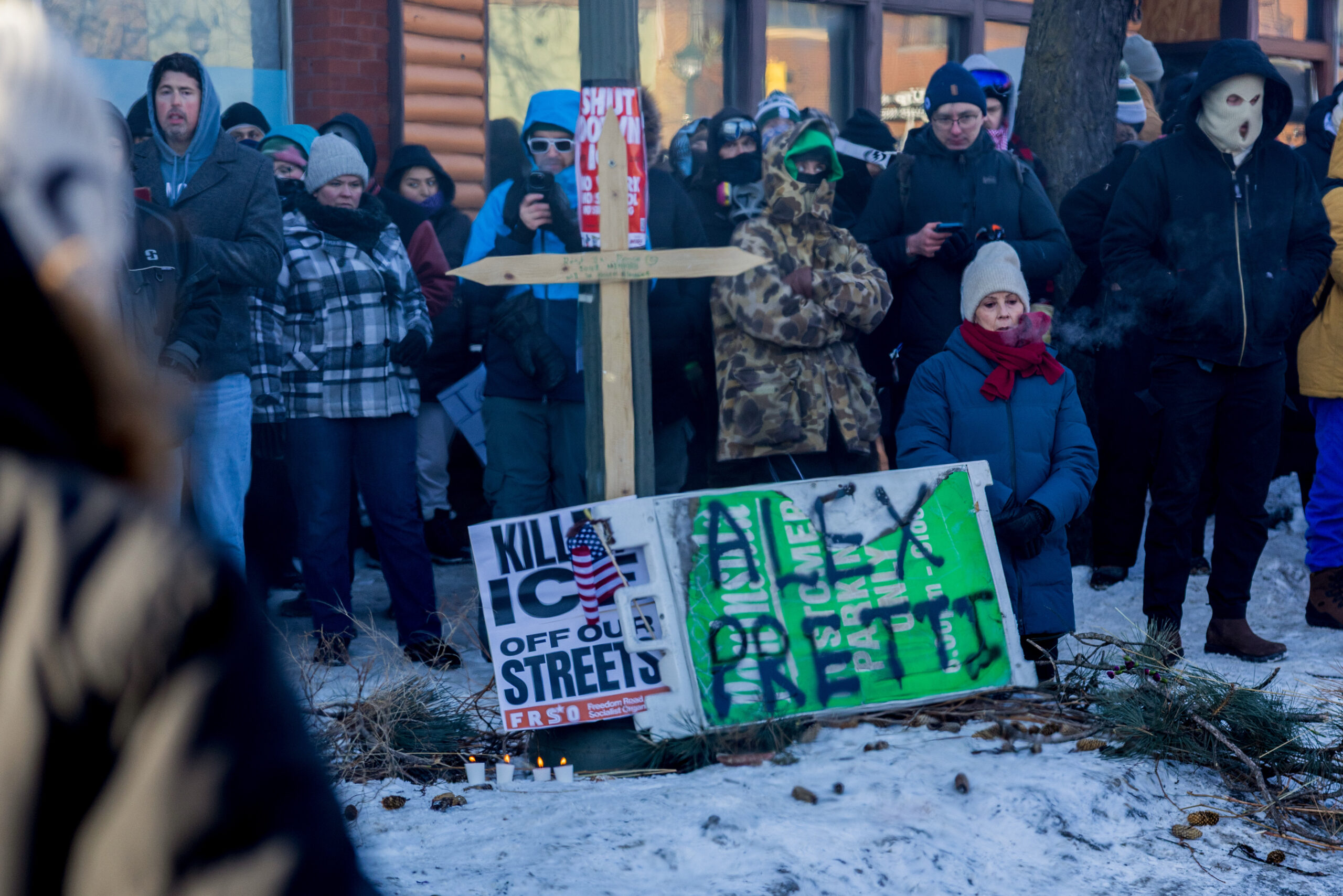
Critics, including the backers of the new legislation, have for months pressed Parker to take a stronger stand.
Brooks said she “would love to have the support of the administration.”
“This should be something that we should be working collaboratively on,” she said. “Philadelphia residents are demanding us do something as elected officials, and this is our time to lead.”
But Parker has not been eager to speak about Philadelphia’s immigration policies.
For example, the city is refusing to release a September letter it sent to the U.S. Department of Justice regarding its immigration-related policies, even after the Pennsylvania Office of Open Records ruled its reasoning for keeping the document secret was invalid. The Inquirer has requested a copy of the letter under the state Right-to-Know Law.
The new Council legislation and the increasing tension over Trump’s deportation push may force Parker to take a clearer position.
Notably, the city sued the federal government last week over its removal of exhibits related to slavery from the President’s House at Independence National Historical Park, potentially signaling a new willingness by Parker to push back against the White House.
But even then, Parker declined to take a jab at Trump.
“In moments like this,” she said last week, “it requires that I be the leader that I need to be for our city, and I can’t allow my pride, ego, or emotions to dictate what my actions will be.”