A three-year ban on puppy breeding in Philadelphia is likely to become law after City Council members on Thursday passed a bill to relieve overcrowded animal shelters.
Lawmakers unanimously approved legislation to institute a three-year moratorium on puppy breeding in the city, a ban that applies to all breeders except those that have a state kennel license or are breeding service dogs.
The bill now heads to Mayor Cherelle L. Parker’s desk. If she signs the bill and it becomes law, the moratorium will take effect 90 days later.
Also on Thursday, a Council member amended his legislation that would allow lawmakers to keep their jobs while running for another office — but there are exceptions.
Here’s what happened during Thursday’s meeting.
What was today’s highlight?
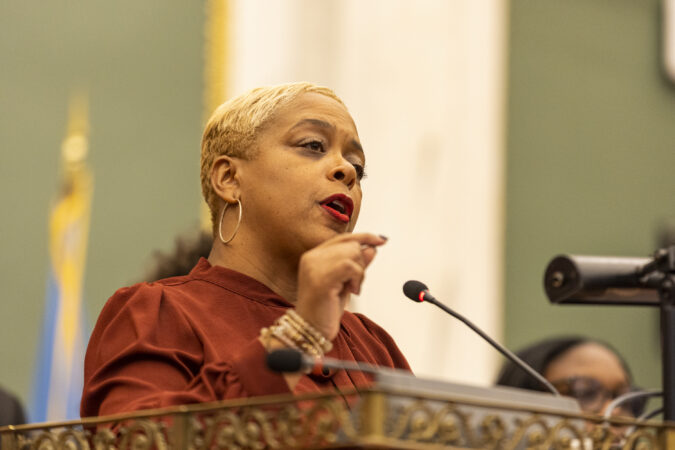
Tightening the leash on backyard breeders: The bill was authored by Councilmember Cindy Bass, a Democrat who represents parts of North and Northwest Philadelphia.
Bass was sick and absent from Council on Thursday, but she has previously said that her bill is aimed at limiting people from breeding more puppies than they can sell.
“Every litter means more dogs in our shelter, more cost for taxpayers, and more suffering that we can prevent,” Bass said last year. “This isn’t about punishment; it’s about compassion and responsibility.”
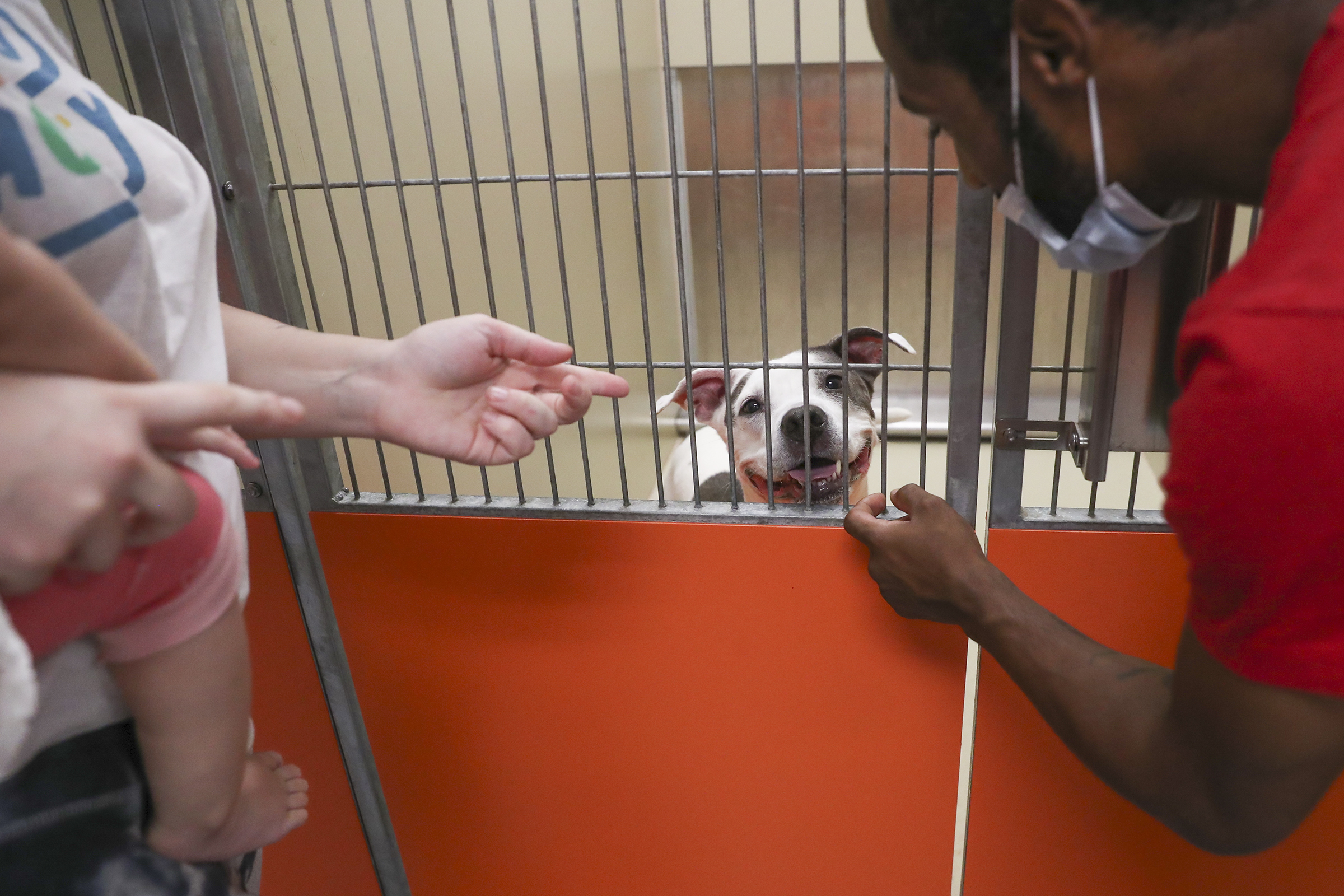
Under the bill, it would be illegal to sell puppies or post ads to sell them within city limits. Breeders who violate the moratorium could face a $1,000 fine, with the proceeds going to the city’s Animal Care and Control Team, also known as ACCT Philly. The animal control agency would also enforce the ban.
Sammi Craven, a local animal welfare advocate, testified Thursday about overcrowding at ACCT Philly’s North Philadelphia shelter. She named the dogs that were recently euthanized or are scheduled to be put down: Stella, Cheese Burrito, Luna, and Muffin, among others.
“Philadelphia’s current animal welfare policy is ineffective,” Craven said, “and infrastructure and prevention have not kept pace with intake.”

Critics of the moratorium say it will be challenging to enforce and could harm smaller, responsible breeders as opposed to those already operating illegally.
Charley Hall, a government relations official with the American Kennel Club, called on Council to hold the bill and establish a working group to draft new regulations.
“Working together, we can stop the flow of irresponsible breeders and improve animal welfare and fewer dogs ending up in Philadelphia’s shelters,” Hall said. “The question is how to achieve that goal in a way that is effective, fair, and legally sound.”
What else happened today?
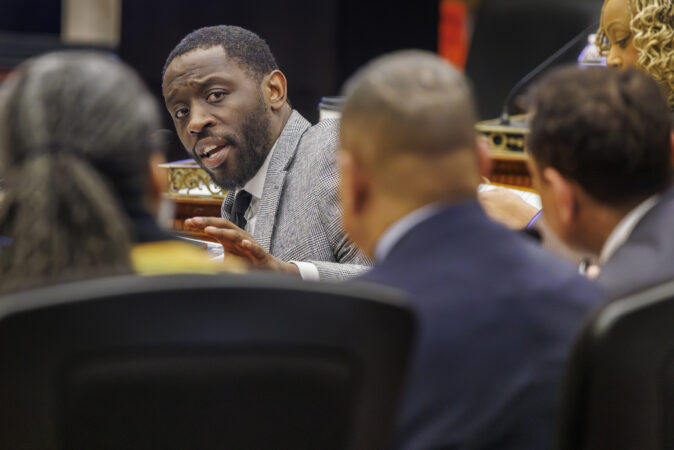
Resign to run gets amended: City Councilmember Isaiah Thomas has been trying for more than a year to pass legislation amending a rule that requires city employees quit their jobs to run for higher office.
He’s attempting to amend the rule so that city officeholders can keep their jobs only if they are running for a state or federal office. That means Council members running for mayor would still have to give up their seats.
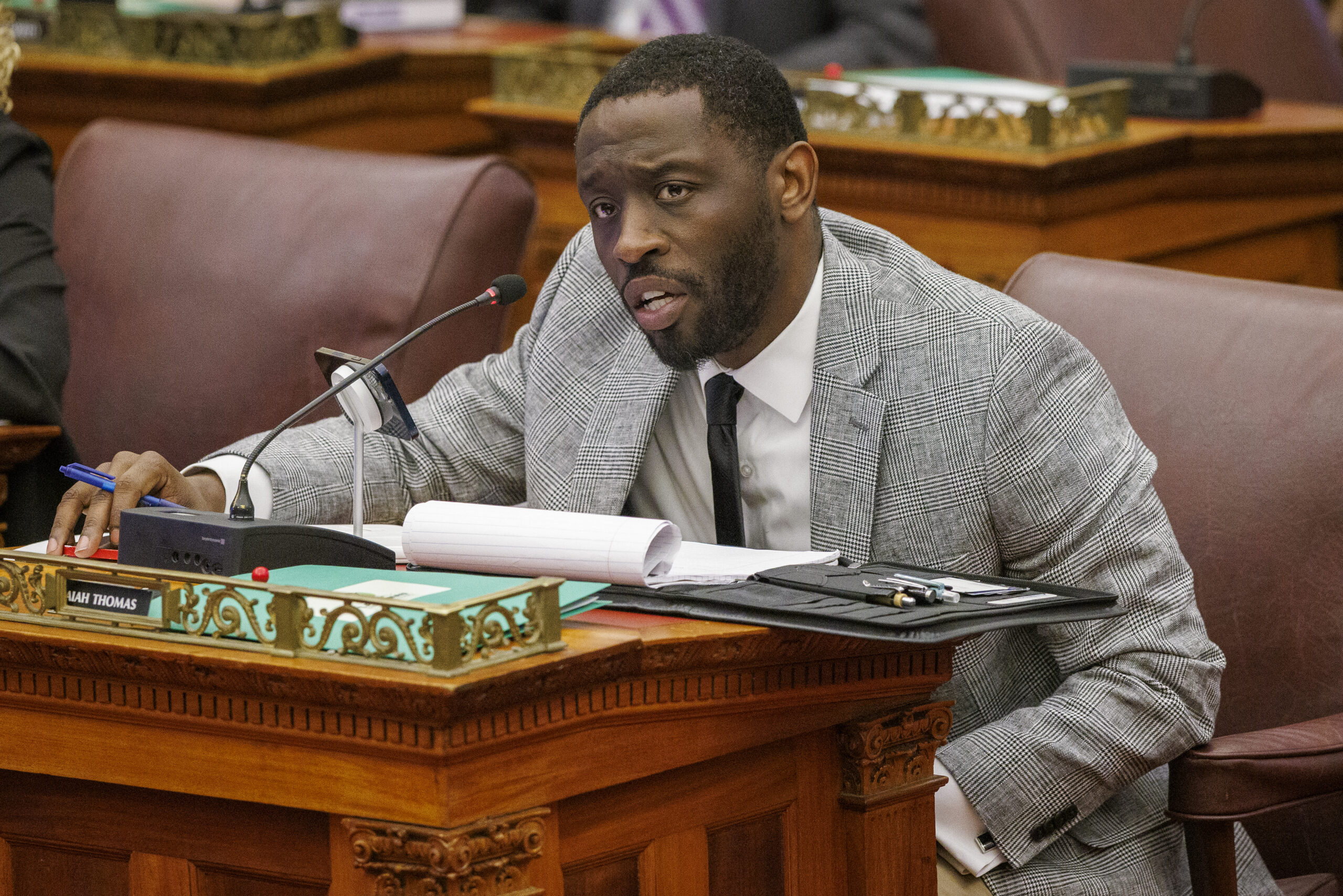

But Thomas has run into roadblocks, including opposition from the city’s Board of Ethics, which asked him to make changes to the legislation in December, just before it appeared poised to pass.
On Thursday, he introduced an amendment that made a series of tweaks, including clarifying that sitting city officeholders may only run for one public office in any election.
Jordana Greenwald, general counsel for the city’s Board of Ethics, testified that the board still has concerns and requested more amendments, including prohibiting certain forms of politicking in the workplace.
She also said the legislation should clarify that the mayor can’t run for another office while serving as the city’s chief executive, a rule that is already enumerated elsewhere in the city charter.
However, making additional amendments could require Thomas re the legislation entirely. He said he would prefer for the bill to be called up for a final vote next week.
Amending the resign-to-run rule requires changing the city’s Home Rule Charter, meaning voters would have to approve it through a ballot question. Voters have rejected earlier attempts to repeal resign-to-run.
Codifying the youth watchdog: Council members also approved legislation to make the city’s Office of the Youth Ombudsperson permanent.
The office was created through an executive order signed by former Mayor Jim Kenney and is responsible for monitoring child welfare, juvenile justice, and behavioral health residential placement facilities in the city.
Making the office permanent also requires an amending the charter. A ballot question is likely to appear in the May primary election.
Quote of the week

That was Councilmember Jim Harrity, an Irish Catholic who in a speech Thursday honored the sacrifices made during the Muslim holy month of Ramadan.