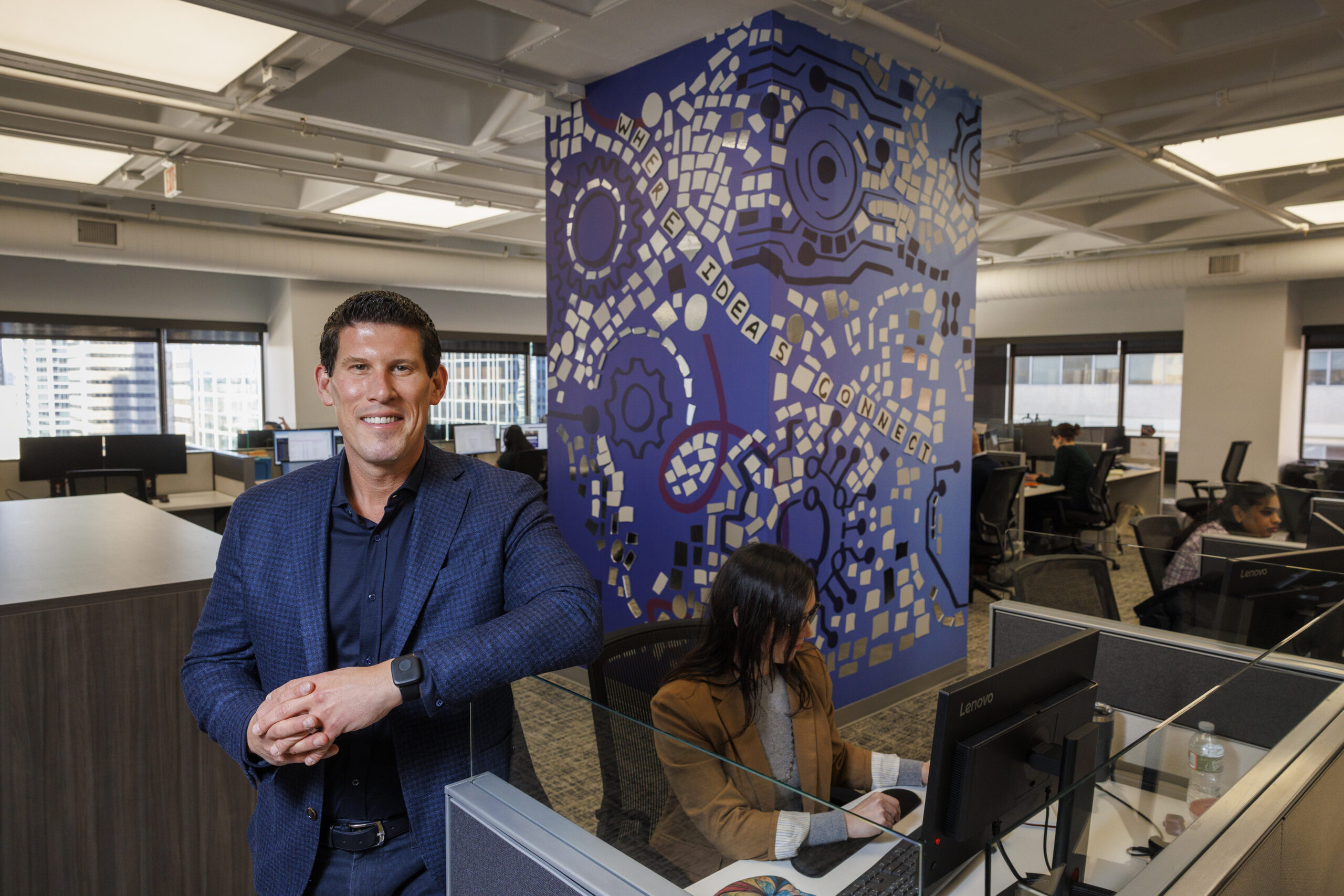
Wawa customers have been able to order roasted chicken on sandwiches, salads, burritos, and more since summer 2024. Hoagie-loving Philadelphians may scroll past the high-protein option on Wawa’s trademarked built-to-order screens, while others tap its icon instinctively in their rush to order lunch.
Wawa CEO Chris Gheysens said he sees the chicken breast differently.
From idea to inception, “that was a labor of love for quite a long time,” Gheysens said in a recent interview. “It’s 37 grams of protein, something consumers are really looking for today.”
And, he added, “it’s still highly customizable, which our customers love doing at Wawa.”
To Gheysens, the menu addition shows how the Delaware County-based company responds to consumer demand. Just as it did decades ago when Philly-area store managers began brewing coffee for customers on the go, and in 1996, when Wawa executives decided to start selling gasoline.
Even now, with nearly 1,200 stores in 13 states and Washington, D.C., Wawa is still listening to consumer feedback, Gheysens said. And despite expanding as far away as Florida and Kentucky, the CEO said, the convenience store giant remains especially in tune with its hometown fans.
“For a lot of people, it’s their daily routine,” said Gheysens, a South Jersey native. “It becomes a part of their neighborhood. It’s a relationship that’s built on consistency, on trust” — and on getting customers out the door in five minutes or less, depending on the time of day.
(function() { var l = function() { new pym.Parent( ‘wawa-stats__graphic’, ‘https://media.inquirer.com/storage/inquirer/ai2html/wawa-stats/index.html’); }; if(typeof(pym) === ‘undefined’) { var h = document.getElementsByTagName(‘head’)[0], s = document.createElement(‘script’); s.type = ‘text/javascript’; s.src = ‘https://pym.nprapps.org/pym.v1.min.js’; s.onload = l; h.appendChild(s); } else { l(); } })();
Customers say they are drawn to the homegrown chain for its convenience, consistency, quality, and wide-ranging menu of grab-and-go and made-to-order items (even though some miss the old Wawa delis where lunchmeat was sliced on the spot).
In Runnemede, 78-year-old Barbara MacCahery said she goes to her local Wawa at least a couple times a week — “sometimes for breakfast, sometimes for a sandwich, a lot of times for coffee.”
In MacCahery’s mind, she said, the chain has proven itself time and time again for decades: “It’s very rare that you’ll have a bad experience.”
Wawa’s ‘secret sauce’ for success

Wawa has set a national standard for success in the convenience store industry, said Z. John Zhang, a marketing professor at the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.
“It really is some kind of a secret sauce,” said Zhang, who studies retail management. “For many people, Wawa has become a destination store,” one that combines “speed, customization, and perceived high quality” with near-constant availability — many Wawa stores are open 24/7.
The company got its start as a dairy, delivering milk to Philly-area households. In 1964, it opened its first store in Folsom. Soon, the family-owned company expanded into New Jersey and Delaware, and established a reputation for quality and speed, with slogans like “People on the Go — Go to Wawa Food Markets.”
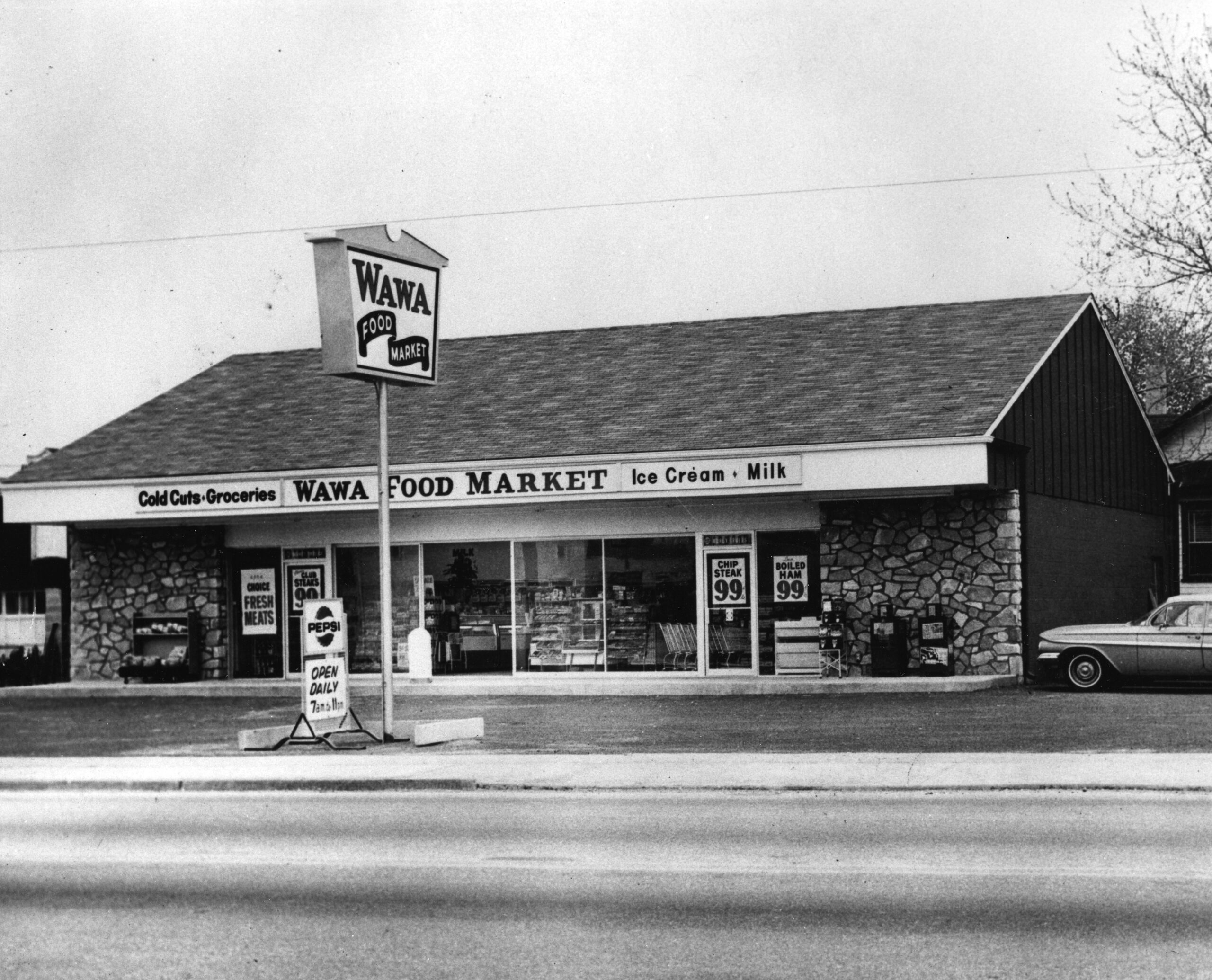

Wawa is privately held, owned in part by workers who get a percentage of their earnings contributed to an employee stock ownership plan. Zhang said this program likely leads to more invested employees who provide better customer service.
Because Wawa is not public, it is not required to disclose its finances, and company executives declined to discuss them.
But by many appearances, Wawa seems to be doing well: Over the past decade, the company has increased its store count by about 65%, and doubled its workforce to about 50,000 associates.
Philly-area Wawas are often crowded, too, which is key to making money in the convenience store industry.

Consumers spend about $7 on average when they stop at a convenience store, said Jason Zelinski, vice president of convenience and growth accounts for NielsenIQ.
“We think it’s high-impulse, but 80% of all people who walk into a convenience store pretty much know what they want,” said Zelinski, who consults with retailers. (He declined to discuss specific companies and said he has never worked for Wawa.)
Successful operators have encouraged customers to spend more by adding seating and improving their food service, Zelinski said. And stores with better food see higher profit margins.
“Once you have somebody that’s addicted to your food service program, they’re more likely to come back to your store vs. a competing store,” he said.

Wawa has certainly gotten people hooked on their coffee, hoagies, and ever-expanding menu, Zhang said. Options added in recent years include pizza, wraps, protein-packed “power meals,” limited-edition coffee flavors, and smoothies “boosted” with protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Yet Wawa hasn’t expanded in all areas.
The company recently closed several stores in Center City, citing “safety and security concerns” in some cases. Last month, it closed its Drexel University location after its test of a digital-order-only format was not successful.
In the Philly suburbs, smaller-format Wawas have also shuttered, often in communities that already have multiple larger Wawas.

Despite Wawa’s best efforts, not all stores thrive, Gheysens said. But “luckily for us, we’re still in growth mode, and don’t have to worry about closures in a broad way.”
Gheysens said he sees room for more Wawas in the Philadelphia market — even as convenience-store competitors like Maryland-based Royal Farms and Altoona-based Sheetz have opened new stores in the region.
Wawa executives want “to make sure that we are the number-one convenience store in the area, that’s important to us,” Gheysens said. “These are our hometown counties.”
What keeps Philly-area consumers going to Wawa

Many Philly-area consumers grew up alongside Wawa.
In interviews with nearly a dozen of them, some were quick to reminisce about early memories of their local stores, such as the distinct smell of coffee and deli meat or the excitement of a Wawa run with high school friends. Others bemoan what has changed with the company’s expansion, including more congested parking lots.
Most have a quick answer when asked what their Wawa order is.
Rick Gunter, 45, of Royersford, misses the Wawa of his youth. Back in the day, he said, the Wawa hoagies “hit different,” with lunchmeat fresh off the slicer.
Contrary to some customers’ beliefs, most stores still bake Amoroso rolls — a custom recipe made exclusively for Wawa — fresh in store multiple times a day, Gheysens said. As for the deli meat, the CEO said that was another decision rooted in customer preference.
When customers have participated in blind tests of the pre-sliced meat Wawa uses today against a fresh-sliced alternative, “they cant’ tell the difference,” Gheysens said. “They would choose our pre-sliced meats, because of what we’ve done in terms of quality and the supply chain and the ability to deliver them at such a pace.”

Some customers disagree.
“It was way better when it was kind of also a deli. Now they try to make everything for everybody,” said Bill Morgan, 79, of East Coventry Township. “I’m within five miles of three Wawas, but I rarely eat their food. Only under extreme duress.”
Morgan acknowledged he must be in the minority, given how crowded Wawas are at lunchtime. And despite his distaste for much of their food, he said he still gets gas there and loves their coffee. And he can’t help but admire their business model.
“I wish they’d sell stock,” Morgan said.